36
original
SUPLEMENTO
Otoneurología 2014:
comprendiendomejor los trastornos vestibulares
Actual.Med.
2014; 99: (791). Supl. 36-60
cured or pickledmeat or fish, red wine and beer. Aspartame, a
sweetener used as a sugar substitute (E951), and monosodium
glutamate, a food additive (E621) used as a flavor enhancer,
are commonmigraine triggers. Patient should identify potential
migraine triggers inorder to avoidor control them; however, we
arenot in favor of amigrainediet. Some triggers areunavoidable
(menstruation) and other can be difficult to detect. Amigraine
diary isusefulandaworksheetofpotential triggersmaybeuseful.
Lifestyle modifications including a regular sleep pattern,
stress reduction by learning how to cope with it (relaxation,
biofeedback,cognitive-behavioural therapy),andaerobicexercise
aregood recommendations. Inmigraineprophylaxis, exercisehas
been demonstrated as effective as drug therapy in reducing the
frequencyofmigraineattacks (20).
PHARMACOTHERAPY
Current preventive treatment is based on the observation
that drug therapy targeted to migraine prophylaxis is also
effective in treating VM. Several studies have reported at least a
50% reduction of the vertiginous episodes frequency at around
80%of thepatients (13, 17, 18, 21, 22). It has beennoted that in
most patientswithVM, vertigo episodes improve in conjunction
withmigraineattacks.
Drugs used for prevention of VM include: anticonvulsants,
antidepressants,
beta-blocker
drugs,
calcium
channel
antagonists, and other agents (table 2). It is thought that most
migraine prophylactic drugs act by increasing the cortical
spreadingdepression threshold, probably throughmodulationof
ion channels, pumps, neurotransmitter receptors, or transporter
genes (23).
Anticonvulsants
Topiramate is a drug that probably acts by multiple
mechanisms: enhancing the inhibitory effects of GABA, blockade
of AMPA/kainate glutamate receptors, by a negativemodulatory
effect on L-typehigh-voltageactivatedCa
2+
channels, blockadeof
voltage-gatedNa
+
channels,and inhibitionofthe IIand IVcarbonic
anhydrase isozymes. Nowadays, it is thought that the mode of
action of topiramate in migraine is related to a modulation of
trigeminovascular transmission within the trigeminothalamic
pathwaywith thekainate receptor beingapotential target.
Very common adverse effects include paresthesia,
somnolence, cognitive slowing, fatigue, dizziness, and weight
loss. These adverse effects occur most frequently in the first
weeks and can bemitigatewith a slow titration. Urolithiasis has
also been associated to topiramate, so patientsmust be advised
to increase theirwater intake.
Valproic acid, sodium valproate and divalproex sodium (or
valproate semisodium, a compound of sodium valproate and
valproic acid) are antiepileptic drugs in which the valproate ion
is the active form. Valproate is a histone-deacetylase inhibitor.
The antiseizure effect is still not fully understood and may be
related with a dual mechanism: blockade of NMDA receptors
attenuating the excitatory action of glutamate and facilitation
of the inhibitory action of GABA. Valproate is also a blocker of
voltage-dependent Na
+
channels, interfering with sustained,
high-frequency, repetitive neuronal firing. Finally, valproate is a
direct inhibitor of histone deacetylases, suggesting onemode of
action is changing gene expression via chromatinmodifications,
and it is alsoanactivator of extracellular signal-regulated kinases
pathway influencing activator protein-1 DNA binding. Through
these later mechanisms valproate could be involved in the
expressionofmultiple genes involved in transcription regulation,
cell survival, ion homeostasis, cytoskeletal modifications and
signal transduction.
Commonadverseeffectsof valproatearenausea, vomiting,
weight gain, tremor and alopecia. Most of these effects can be
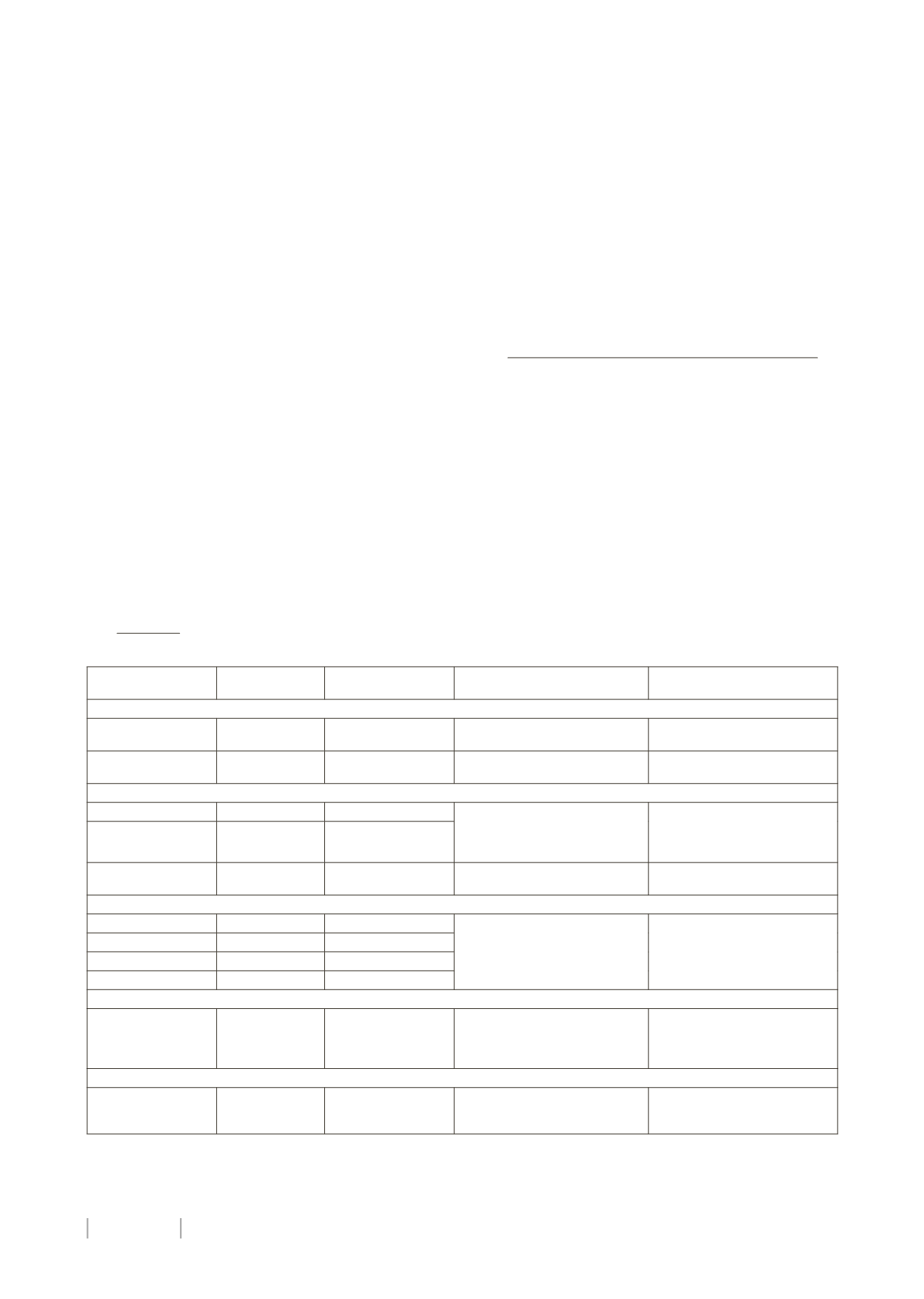
Startingdose Recommended
dose
Adverseeffects
Precautions/
contraindications
Anticonvulsants
topiramate
15-25mg/24h 50mg/12h
paresthesia
weight loss
urolithiasis, kidney failure
depression
valproate
300mg/24h
600mg/24h
nausea&vomiting
weight gain
liver disease, pregnancy
Antidepressants
amitriptyline
10mg/24h
25-75mg/24h
weight gain
drowsiness
hypotension
drymouth
heart disease
nortriptyline
venlafaxine
37,5mg /24h 37,5mg /12h
Nausea, drymouth, headaches,
drowsiness
bipolar disorder, IMAOs
Beta-blockers
propranolol
20mg/12h
40-80mg/12h
fatigue, bradycardia,
hypotension, bronchospasm,
impotence
diabetes, ischemic
cardiomyopathy, asthma
metoprolol
25mg/12h
50-100mg/12h
nadolol
20-40mg/24h 40-80mg/24h
atenolol
50mg/ 24h
50-100mg/24h
Calcium channel antagonists
flunarizine
2,5-5mg/24h 5-10mg/24h
weight gain
depression
somnolence
parkinsonism
depression, Parkinson´s
disease
Other drugs
acetazolamide
250mg/24h
500 -750mg
paresthesia,
hypokalemia
urolithiasis, hyperchloremic
metabolicacidosis, depression,
kidneyor liver failure
Table2. Preventivemedication investibularmigraine.


